
Enzymes are important for catalyzing all types of biological reactions-those that require energy as well as those that release energy. Each reaction step is facilitated, or catalyzed, by a protein called an enzyme. It is important to know that the chemical reactions of metabolic pathways do not take place on their own.
Consequently, metabolism is composed of synthesis (anabolism) and degradation (catabolism) ( Figure 4.3). These two opposite processes-the first requiring energy and the second producing energy-are referred to as anabolic pathways (building polymers) and catabolic pathways (breaking down polymers into their monomers), respectively. In the example of sugar metabolism, the first metabolic pathway synthesized sugar from smaller molecules, and the other pathway broke sugar down into smaller molecules.
#Stored energy process 3 steps in human body series
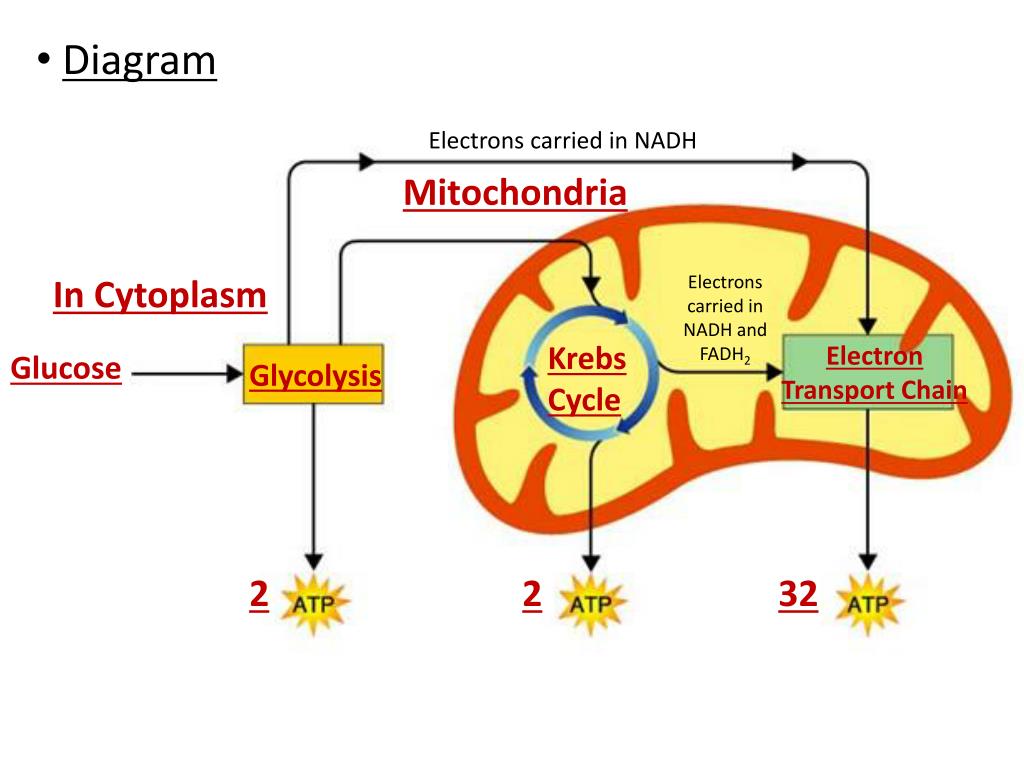
A metabolic pathway is a series of chemical reactions that takes a starting molecule and modifies it, step-by-step, through a series of metabolic intermediates, eventually yielding a final product. The processes of making and breaking down sugar molecules illustrate two examples of metabolic pathways. The reaction is summarized as:Ĭ 6H 12O 6 + 6O 2 -> 6CO 2 + 6H 2O + energyīoth of these reactions involve many steps. In this reaction, oxygen is consumed and carbon dioxide is released as a waste product. The reaction that harvests the energy of a sugar molecule in cells requiring oxygen to survive can be summarized by the reverse reaction to photosynthesis. In contrast, energy-storage molecules such as glucose are consumed only to be broken down to use their energy. Just as the dollar is used as currency to buy goods, cells use molecules of ATP as energy currency to perform immediate work. During the light reactions of photosynthesis, energy is provided by a molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the primary energy currency of all cells.

This reaction is summarized as:ĦCO 2 + 6H 2O + energy -> C 6H 12O 6+ 6O 2īecause this process involves synthesizing an energy-storing molecule, it requires energy input to proceed. They consume carbon dioxide and produce oxygen as a waste product. During photosynthesis, plants use energy (originally from sunlight) to convert carbon dioxide gas (CO 2) into sugar molecules (like glucose: C 6H 12O 6). For the most part, photosynthesizing organisms like plants produce these sugars. Living things consume sugars as a major energy source, because sugar molecules have a great deal of energy stored within their bonds. This is a classic example of one of the many cellular processes that use and produce energy. Metabolic PathwaysĬonsider the metabolism of sugar. Carnivores eat the herbivores, and eventual decomposition of plant and animal material contributes to the nutrient pool. Plants use photosynthesis to capture sunlight, and herbivores eat the plants to obtain energy. Figure 4.2 Ultimately, most life forms get their energy from the sun. Together, all of the chemical reactions that take place inside cells, including those that consume or generate energy, are referred to as the cell’s metabolism.

Just as living things must continually consume food to replenish their energy supplies, cells must continually produce more energy to replenish that used by the many energy-requiring chemical reactions that constantly take place. Some of these chemical reactions are spontaneous and release energy, whereas others require energy to proceed. Cellular processes such as the building and breaking down of complex molecules occur through stepwise chemical reactions. Scientists use the term bioenergetics to describe the concept of energy flow ( Figure 4.2) through living systems, such as cells.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
